Electric Muscle Stimulation (EMS) is a technology that stimulates muscle contractions through electrical impulses. These devices are useful for muscle recovery, muscle strengthening, and pain management. Electric Muscle Stimulation has been used in physical therapy and sports medicine for decades, but with advances in technology, Electric Muscle Stimulation devices are now widely available for personal use.
Electric Muscle Stimulation has gained popularity as a way to enhance workout performance and build muscle faster, but understanding the risks and benefits, as well as how to properly use an Electric Muscle Stimulation device, is essential to preventing injury.
What is Electrical Muscle Stimulation?
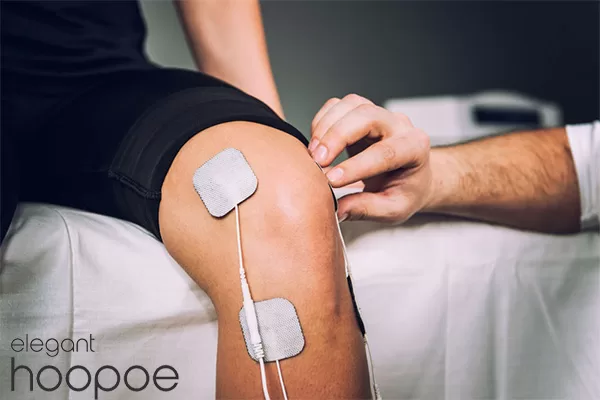
Electrical muscle stimulation (EMS) is a type of therapy that involves the use of electrical impulses to stimulate the muscles. Electric Muscle Stimulation is also called neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) or electromyostimulation. By placing electrodes on the skin over the muscle group being stimulated, electrical impulses are delivered. As well as improving muscle function, strength, and endurance, Electric Muscle Stimulation promotes circulation and relieves pain.
Electric impulses cause the muscles to contract. These contractions are similar to voluntary muscle contractions, but they are stronger and more frequent than voluntary contractions. Depending on the desired outcome, electrical impulses can be adjusted at different frequencies and intensities. Lower frequencies may be used to reduce pain, while higher frequencies may be used to build strength and endurance.
EMS is used in a wide variety of settings, including physical therapy, sports training, and rehabilitation. It can be used for individuals with muscle weakness or atrophy, as well as those recovering from injuries or surgeries. It can also be used to enhance muscle development and improve overall fitness as a complement to traditional exercise programs.
While Electric Muscle Stimulation can be a beneficial therapy for many individuals, it is important to note that it should be used under the guidance of a trained professional. Electric Muscle Stimulation can damage muscle tissues or cause other complications if it is used improperly. Before starting EMS, it is important to discuss its risks and benefits with your healthcare provider.

What are muscle stimulation electrodes?
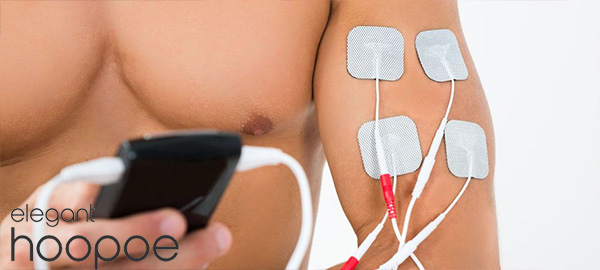
Electrodes for electrical muscle stimulation (EMS) are small adhesive pads with conductive materials such as carbon that transmit electrical impulses from Electric Muscle Stimulation devices to the muscles.
In addition to coming in a variety of shapes and sizes, muscle stimulation electrodes can be placed anywhere on the body depending on the muscle being targeted. Through wires or cables, they are connected to the Electric Muscle Stimulation device using an adhesive, and they are usually attached to the skin with an adhesive.
As Electric Muscle Stimulation therapy proceeds, the muscles contract and relax due to the electrical impulses delivered by the electrodes. Individuals who are unable to participate in traditional exercise because of injury, illness, or mobility limitations may find this useful. Electrical impulses can trigger muscle contractions, thereby providing a more intense workout than voluntary muscle contractions alone can.
Muscle stimulation electrodes must be used correctly to ensure safety and effectiveness. It is important to select the right size and shape electrodes for the specific muscle group being targeted, followed by following the manufacturer’s instructions on how to place, intensify, and use the electrodes. To ensure that there are no signs of irritation or other adverse reactions during Electric Muscle Stimulation therapy, it is also crucial to monitor the skin regularly.
Read more: 6 effective ways to lose belly fat and keep it off
How does muscle stimulation work?
Electric impulses are delivered to the muscles through electrodes attached to the skin. The electrodes are connected to a device that generates the electrical impulses. The device can be adjusted to control the frequency, duration, and intensity of the electrical impulses.
In the same way that the nervous system stimulates muscles to contract when electrical impulses are delivered to them, the muscles contract as a result of the electrical impulses. Over time, repeated contractions caused by muscle stimulation can increase muscle strength and endurance.
The use of muscle stimulation in physical therapy is often used to help patients recover after injuries or surgeries that affect their muscles. In addition to helping athletes improve their performance, it can also be used to prevent muscle atrophy in patients who are unable to exercise because of injury or illness.
Electrical muscle stimulation benefits
In electrical muscle stimulation (EMS), electrical impulses are used to stimulate the contraction of muscles, and this therapy has a wide range of potential benefits, particularly for people who suffer from muscle weakness, atrophy, injuries, or chronic pain.
EMS has the primary benefit of strengthening and toning muscles. By triggering muscle contractions using electrical impulses, Electric Muscle Stimulation can provide an intense workout that is not possible through voluntary muscle contractions alone. People who are unable to engage in traditional exercise due to injury, illness, or mobility limitations can particularly benefit from this.
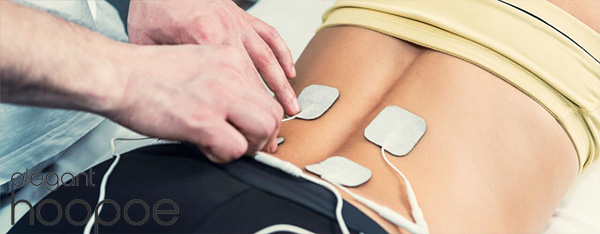
Pain relief can also be achieved with EMS. Electrical impulses used in Electric Muscle Stimulation can help block pain signals from reaching the brain, providing temporary relief from chronic pain conditions like arthritis, fibromyalgia, and back pain. Further, Electric Muscle Stimulation can increase blood flow and accelerate the recovery process by reducing inflammation and increasing blood flow in injured tissues.
As well as improving range of motion and flexibility, Electric Muscle Stimulation may also improve athletic performance. Physical therapy clinics, sports training facilities, and even some at-home devices have used EMS. In general, Electric Muscle Stimulation is considered safe when used appropriately, but prior to beginning any new therapy or exercise program, you should consult your healthcare professional.
Common applications of electrical muscle stimulation
Electrical muscle stimulation has found a wide range of applications in both fitness and rehabilitation settings. In the fitness realm, EMS is often used as a supplement to traditional exercise routines. It can be incorporated into strength training workouts to enhance muscle activation and increase the intensity of training sessions. EMS is also commonly used in sports performance enhancement programs to improve explosive power and agility.
In the rehabilitation field, EMS is utilized in physical therapy settings to aid in muscle recovery and re-education. It can be used to prevent muscle atrophy in individuals who are immobilized due to injury or surgery. Furthermore, EMS can be effective in rehabilitating muscles after surgery or in individuals with neurological conditions that affect muscle function.
The science behind electrical muscle stimulation
The science behind electrical muscle stimulation lies in the principle of neuromuscular electrical stimulation. When electrical impulses are delivered to the muscles, they trigger a response in the motor neurons, which then send signals to the muscle fibers, causing them to contract. This process is similar to the way our brain communicates with our muscles during voluntary movements.
By applying electrical currents to the muscles, EMS bypasses the need for the brain to initiate muscle contractions. This allows for a more targeted and controlled stimulation of the muscles. The intensity and frequency of the electrical impulses can be adjusted to activate specific muscle fibers and achieve desired outcomes.
Safety considerations and precautions
While electrical muscle stimulation can be a highly effective tool, it is important to use it safely and responsibly. Before starting an EMS program, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or fitness expert to ensure it is suitable for your individual needs and goals. They can provide guidance on the appropriate intensity and frequency of electrical impulses and help you avoid potential risks or complications.
It is also crucial to follow the manufacturer’s instructions when using an EMS device. Proper electrode placement and skin preparation are essential to ensure optimal results and minimize the risk of skin irritation. Additionally, it is important to start with lower intensity levels and gradually increase the intensity as your muscles become accustomed to the stimulation.
Choosing the right electrical muscle stimulation device
When selecting an electrical muscle stimulation device, there are several factors to consider. First and foremost, it is important to choose a device that is FDA-approved or CE-certified. This ensures that the device meets safety and quality standards. Additionally, look for a device that offers customizable settings, allowing you to adjust the intensity and frequency of the electrical impulses to suit your individual needs.
Comfort and ease of use are also important considerations. Look for a device that comes with high-quality electrodes that are comfortable to wear and easy to position on the target muscles. A device with a user-friendly interface and clear instructions will make your EMS workouts more enjoyable and effective.
What are the risks of electro muscle stimulation?
Electric muscle stimulation (EMS) can have numerous benefits, but it can also carry some risks. These risks will vary depending on the individual and the specific circumstances involved.
A significant risk associated with Electric Muscle Stimulation is muscle damage. Electric shocks used in Electric Muscle Stimulation are very intense, so they are capable of causing muscle tears, strains, or other types of injury. Electric Muscle Stimulation devices can increase this risk if they aren’t used properly or if they’re used on muscles that are already weakened or injured.
EMS can also cause skin irritation or burns. When the electrodes are not placed properly or used for too long at a high intensity level, they can cause skin irritation or even burns. To ensure that there are no signs of irritation during Electric Muscle Stimulation therapy, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully and to check the skin regularly.
Also, in rare cases, Electric Muscle Stimulation can cause seizures, arrhythmias, or nerve damage in patients. Generally, these complications are caused by improper use of the device, or by individuals with pre-existing medical conditions that make them more at risk of them.
Prior to beginning any new therapy or exercise program, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to minimize the risks associated with EMS. Electric Muscle Stimulation therapy can be safely and appropriately administered by a trained healthcare professional who can assess a patient’s needs and risks.
Tips for effective electrical muscle stimulation workouts
To get the most out of your electrical muscle stimulation workouts, consider incorporating these tips:
- Warm up: Prior to starting your EMS session, warm up your muscles with dynamic stretches or light aerobic exercise. This helps to prepare your muscles for the upcoming contractions and reduces the risk of injury.
- Focus on form: Pay attention to your body alignment and posture during EMS workouts. Proper form ensures that the electrical impulses are effectively targeting the desired muscles and reduces the risk of imbalances or strains.
- Combine with traditional exercise: While EMS can be highly effective on its own, combining it with traditional exercise can further enhance your results. Consider incorporating EMS into your existing workout routine, alternating between EMS sessions and traditional strength training or cardiovascular exercises.
Conclusion
Electrical muscle stimulation is a powerful technology that can revolutionize your fitness routine and aid in rehabilitation. By understanding how EMS works and its potential applications, you can make informed decisions about incorporating this innovative technique into your training program. Remember to prioritize safety, consult with experts, and choose the right EMS device for your needs. With proper usage and consistency, electrical muscle stimulation can help you unlock your full potential and achieve your health and fitness goals.