Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the body is unable to regulate blood sugar levels properly, either due to a lack of insulin production or the body’s inability to use insulin effectively. While medication and lifestyle changes can help manage diabetes, losing weight has been shown to have a significant impact on improving blood sugar control. But is weight loss good for diabetes?
While genetics and other factors play a role in its development, research has consistently shown that weight is a significant risk factor for both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Obesity is one of the most common risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes, with overweight individuals being twice as likely to develop the condition compared to those at a healthy weight.
In this article on Elegant Hoopoe, we will explore the link between weight loss and diabetes, how losing weight can improve diabetes control, and examine the benefits and potential risks of weight loss for a diabetic.
What is the link between body weight and diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. This insulin resistance is often associated with being overweight or obese. When excess fat is stored in the body, it can interfere with the body’s ability to use insulin effectively, leading to high blood sugar levels and eventually, the development of type 2 diabetes.
Additionally, excess weight can cause inflammation in the body, which can further contribute to insulin resistance and diabetes. Inflammation can also damage blood vessels and lead to other health complications associated with diabetes, such as heart disease and stroke.
How does weight loss affects diabetes?
On the other hand, losing weight diabetes type 2 can significantly improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control in people with diabetes. Even a modest weight loss of 5% to 10% of one’s total body weight can make a significant difference in diabetes management. Weight loss can also improve blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and overall cardiovascular health, which are important considerations for people with diabetes who are at higher risk for these conditions.
Read more: weight loss and blood pressure, what is the link?
Overall, the link between weight and diabetes is clear, and weight loss can be an effective tool in managing the condition. By adopting healthy habits like eating a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity, individuals with diabetes can improve their overall health and potentially even achieve remission of the condition.
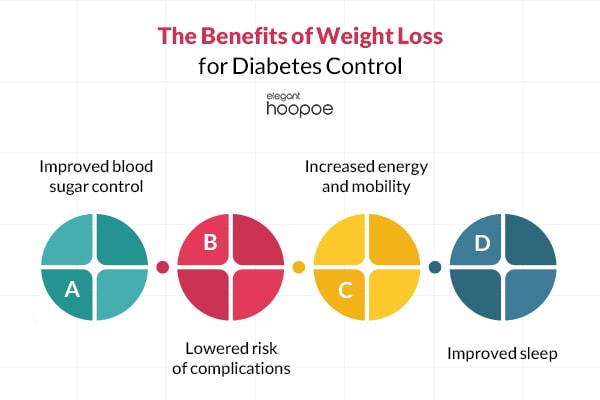
The Benefits of Weight Loss for Diabetes Control
Lose weight diabetes can be very beneficial for controlling diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes. When a person loses weight, it can improve insulin sensitivity and help the body use insulin more effectively to regulate blood sugar levels. Here are some of the weight loss benefits for diabetes control:
Improved blood sugar control
Weight loss can lead to a decrease in blood sugar levels, reducing the need for medication or insulin injections.
Reduced insulin resistance: Losing weight can improve the body’s ability to use insulin and reduce insulin resistance, which can also lead to better blood sugar control.
Lowered risk of complications
Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the risk of developing complications associated with diabetes, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and nerve damage.
Increased energy and mobility
Losing weight can improve physical activity levels, energy levels, and overall quality of life for people with diabetes.
Improved sleep
Weight loss can lead to improved sleep patterns, which can be particularly beneficial for people with diabetes who may have sleep disturbances due to high blood sugar levels.
Overall, weight loss is an important part of diabetes management and can lead to significant improvements in blood sugar control and overall health. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to develop a safe and effective weight loss plan that is tailored to individual needs and health status.
Potential Risks
While weight loss can have many benefits for people with diabetes, there are also potential risks to consider. These risks can include:
Hypoglycemia
Losing weight can affect blood sugar levels, and people with diabetes who take medication or insulin may be at risk for hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) if they do not adjust their medication doses accordingly.
Nutrient deficiencies: Restricting calories and certain food groups can lead to nutrient deficiencies, particularly if the person is not careful to consume a balanced diet with adequate vitamins and minerals.
Muscle loss
Losing weight can lead to a loss of muscle mass, which can affect overall strength and fitness.
Gallstones
Rapid weight loss can increase the risk of gallstones, particularly in people who are overweight or obese.
Malnutrition
Severely restricting calories can lead to malnutrition, which can have negative impacts on overall health.
Eating disorders
People with diabetes may be at increased risk for developing disordered eating patterns or eating disorders as a result of the focus on food and weight management in diabetes management.
It is important to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan for weight loss that takes into account individual needs and circumstances and to monitor for any potential risks or complications. A gradual and sustainable approach to weight loss is typically recommended to minimize the risks associated with rapid weight loss.
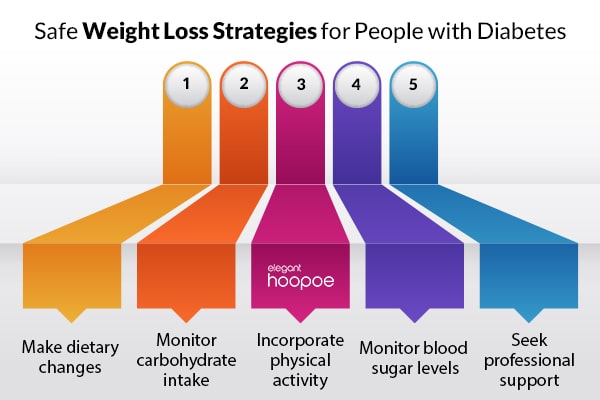
Safe Weight Loss Strategies for People with Diabetes
Safe weight loss strategies for people with diabetes include making gradual lifestyle changes that promote healthy eating habits and regular physical activity. Here are some tips:
- Make dietary changes: Focus on incorporating more nutrient-dense, low-calorie foods into your diet, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit your intake of processed and high-calorie foods, such as sugary drinks, snacks, and desserts.
- Monitor carbohydrate intake: Carbohydrates can have a significant impact on blood sugar levels, so it is important to monitor your carbohydrate intake and choose healthier, low-glycemic index options. This can involve choosing complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, and limiting simple carbohydrates, such as refined sugars.
- Incorporate physical activity: Regular physical activity can help promote weight loss and improve blood sugar control. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity, such as brisk walking or cycling, per week. Resistance training can also be beneficial for building muscle mass and improving overall fitness.
- Monitor blood sugar levels: As you make changes to your diet and physical activity levels, it is important to monitor your blood sugar levels regularly to ensure they remain within a healthy range.
- Seek professional support: Working with a healthcare provider, registered dietitian, or diabetes educator can provide guidance and support for developing a safe and effective weight loss plan.
It is important to approach weight loss with a long-term perspective and focus on making sustainable lifestyle changes that promote overall health and well-being. Crash diets or fad diets that promise quick weight loss can be dangerous and ineffective in the long term.
Can Weight Loss Lead to Remission of Type 2 Diabetes?
Yes, weight loss can lead to the remission of type 2 diabetes in some cases. Remission refers to a state where blood sugar levels return to normal without the need for medication or insulin injections.
Research suggests that achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control, which can lead to the remission of type 2 diabetes. In some cases, weight loss may be the only intervention needed to achieve remission.
However, it is important to note that not all cases of type 2 diabetes can be cured or managed solely through weight loss. Some people with type 2 diabetes may require medication or insulin even with weight loss and lifestyle changes.
The goal should be to achieve and maintain a healthy weight through sustainable lifestyle changes, such as healthy eating habits and regular physical activity, to improve overall health and prevent the progression of type 2 diabetes.
Addressing Concerns
Weight loss can be an effective strategy for managing diabetes, but it is important to address any concerns that people may have about it. Here are some common concerns and how to address them:
Fear of hypoglycemia
People with diabetes may be concerned that weight loss could lead to low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia). However, with careful monitoring and adjustment of medication or insulin doses as needed, the risk of hypoglycemia can be minimized. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan that takes into account individual blood sugar levels and medication needs.
Difficulty with dietary changes
Changing eating habits can be challenging, especially if a person is used to a certain way of eating. However, dietary changes do not have to be drastic or restrictive. Gradual changes, such as incorporating more fruits and vegetables, choosing lean proteins, and limiting sugary and high-calorie foods, can make a difference. Working with a registered dietitian can provide guidance and support for making dietary changes that are sustainable and enjoyable.
Concerns about physical activity
Some people with diabetes may have concerns about physical activity, such as fear of injury or exacerbating other health conditions. However, regular physical activity can have numerous benefits for diabetes management, including improved blood sugar control, weight loss, and cardiovascular health. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to develop a safe and appropriate exercise plan that takes into account individual health status and goals.
Frustration with slow progress
Weight loss can be a slow process, and it can be frustrating if progress is not immediate or significant. However, even modest weight loss can lead to improvements in blood sugar control and overall health. Celebrating small successes and focusing on long-term progress can help maintain motivation and momentum.
It is important to approach weight loss with a long-term perspective and focus on making sustainable lifestyle changes that promote overall health and well-being. Working with a healthcare provider, registered dietitian, or diabetes educator can provide guidance and support for developing a safe and effective weight loss plan.
Diet and Exercise for Diabetics
Diet and exercise are essential components of weight loss for diabetes control. A healthy diet and regular exercise are essential components of weight loss for diabetes control. The goal should be to make sustainable lifestyle changes that promote overall health and well-being and improve blood sugar control over the long term. Here’s how they can help:
Diet
A healthy diet can help manage blood sugar levels, reduce body weight, and improve overall health. People with diabetes should aim for a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. It is also important to limit sugary and high-calorie foods, as they can cause spikes in blood sugar levels and contribute to weight gain.
Read more: Surgical weight loss vs diet and exercise, which is more effective and better in long terms?
Exercise
Regular exercise can help burn calories, improve insulin sensitivity, and lower blood sugar levels. People with diabetes should aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity, such as brisk walking or cycling, per week. Resistance training can also be beneficial for building muscle mass and improving overall fitness.
Combination
The combination of diet and exercise is more effective than either alone for weight loss and diabetes control. A calorie-controlled diet combined with regular physical activity can help create a calorie deficit that leads to weight loss while improving blood sugar control.
Consistency
Consistency is key to success. It is important to make sustainable lifestyle changes that can be maintained over the long term. Crash diets or extreme exercise regimens may produce rapid weight loss but are unlikely to be sustainable and can be harmful.
Monitoring
It is important to monitor blood sugar levels and adjust medication or insulin doses as needed when making dietary and exercise changes. Consulting with a healthcare provider, registered dietitian, or diabetes educator can provide guidance and support for developing a safe and effective weight loss plan.

Weight loss surgery and medications for diabetes
Medications or surgery may be considered for weight loss in people with diabetes if lifestyle changes alone are not sufficient or if the person has significant obesity-related health problems. Here are some considerations for when to consider medications or surgery for weight loss:
Medications
Weight loss medications may be prescribed for people with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher, or those with a BMI of 27 or higher with obesity-related health problems such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or sleep apnea. These medications work by suppressing appetite or blocking the absorption of fat. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to determine if medications are appropriate and safe.
Bariatric surgery
Bariatric surgery may be considered for people with a BMI of 40 or higher, or those with a BMI of 35 or higher with obesity-related health problems such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or sleep apnea. This procedure can help people lose weight by reducing the size of the stomach or bypassing part of the digestive tract. This leads to a reduced ability to consume and absorb food, resulting in weight loss. Bariatric surgery is a major surgery and requires careful consideration and evaluation by a healthcare provider.
Risks and benefits
Medications and surgery for weight loss have risks and benefits that should be carefully considered. Risks may include side effects, complications, and the need for ongoing monitoring and follow-up care. Benefits may include improved blood sugar control, reduced risk of obesity-related health problems, and improved quality of life.
Individual factors: The decision to use medications or surgery for weight loss should be based on individual factors such as overall health, goals, and preferences. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan that takes into account individual needs and circumstances.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, weight loss is an important aspect of diabetes management, particularly for people with type 2 diabetes. Losing weight can improve blood sugar control, reduce the risk of diabetes-related health problems, and improve the overall quality of life.
A combination of healthy eating, regular physical activity, and behavior modification can promote sustainable weight loss and improve diabetes management. However, it is important to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan that takes into account individual needs and circumstances.
In some cases, medications or surgery may be considered for weight loss, but lifestyle changes should always be the first line of treatment. Maintaining healthy habits is essential for long-term diabetes management and overall health and well-being.