What Is the Ideal Fat to Muscle Ratio—and How Do You Achieve It?
Your fat to muscle ratio is key to better health, faster metabolism, and a lean physique. Here’s how to improve it:
- Build muscle with strength training
- Burn fat through cardio
- Eat protein-rich foods
- Maintain a mild calorie deficit
- Prioritize rest and sleep
Achieve the ideal fat to muscle ratio with consistency, smart training, and proper nutrition.
The fat-to-muscle ratio is a crucial measurement that reflects the proportion of body fat compared to muscle mass in the human body. This ratio not only influences physical appearance but also plays a pivotal role in overall health, metabolic efficiency, and physical performance. Achieving an optimal balance between fat and muscle is essential for enhancing both aesthetics and longevity. In this article, we will explore the science behind fat-to-muscle ratio, why it matters, and how you can improve it to reach a healthier body composition balance.

Understanding Body Composition Balance
Body composition balance refers to the relative proportion of fat mass and lean mass (which includes muscle, bones, organs, etc.) in the body. Maintaining an ideal fat to muscle ratio is essential for overall health, as too much fat, particularly visceral fat (fat around organs), can increase the risk of various diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and metabolic disorders. Meanwhile, muscle mass plays a critical role in boosting metabolism, strength, and overall function.
Achieving the right balance between fat and muscle is not just about aesthetics; it significantly impacts how your body performs, how it recovers from exercise, and how efficiently it processes nutrients. Whether you are aiming to look more toned, lose fat, or simply improve your health, understanding body composition balance is the key.

The Science Behind Fat to Muscle Ratio
To truly understand the importance of the fat to muscle ratio, it’s essential to first understand the science behind body composition. The human body is made up of fat mass and lean mass. Lean mass includes muscle tissue, bones, and organs, while fat mass is the body fat stored in subcutaneous and visceral regions.
Essential Fat vs. Storage Fat
- Essential Fat: This type of fat is critical for normal bodily functions, such as hormone regulation, temperature control, and organ protection. Both men and women have essential fat, but women typically need a higher percentage for reproductive health.
- Storage Fat: This is the excess fat stored in the body, primarily for energy reserves. It’s located beneath the skin (subcutaneous fat) and around internal organs (visceral fat). Excessive storage fat, particularly visceral fat, is linked to various health risks, including cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes.
The fat to muscle ratio helps you understand how much fat is stored in your body compared to how much lean tissue you have. Maintaining an appropriate ratio ensures that you’re not carrying excessive fat while having enough muscle mass for optimal function.
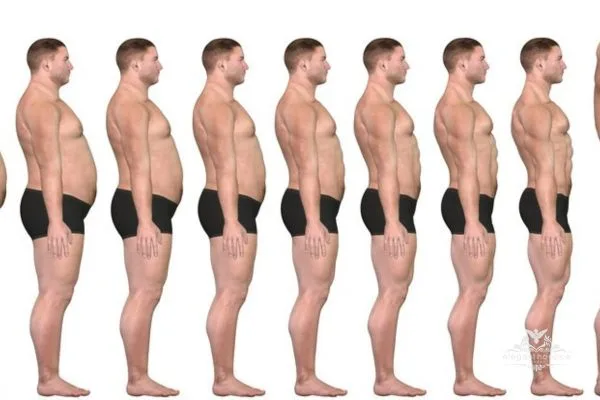
Why is the Fat-to-Muscle Ratio Important?
Achieving a healthy fat to muscle ratio has several important benefits that affect both appearance and overall health.
Boosting Metabolism
Muscle tissue burns more calories at rest compared to fat. The more muscle mass you have, the higher your metabolic rate. This means you’ll burn more calories even when you’re not working out, which is crucial for weight management.
Improved Physical Performance
Having more muscle mass enhances your strength, endurance, and overall physical performance. Whether you’re lifting weights, running, or doing daily activities, the right fat-to-muscle ratio can improve your ability to perform and recover from physical exertion.
Better Health Outcomes
An optimal fat to muscle ratio can improve health markers like cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and insulin sensitivity. Achieving a favorable body composition is linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases such as obesity, heart disease, and type 2 diabetes.
Enhanced Aesthetics
A lower body fat percentage paired with well-developed muscle mass leads to a leaner, more toned appearance. Many people strive to improve their fat-to-muscle ratio for aesthetic reasons, as a balanced composition enhances muscle definition and overall physique.
How to Measure Your Fat to Muscle Ratio
Measuring your fat-to-muscle ratio is a crucial first step in assessing your body composition. There are several methods available to track changes in body fat and lean mass over time:
Body Fat Percentage Measurement
Body fat percentage indicates how much of your total body weight is fat. It can be measured using methods like skinfold calipers, bioelectrical impedance scales, or more advanced techniques like DEXA scans. Understanding your body fat percentage helps determine if you have an optimal fat to muscle ratio.
Skinfold Calipers
This tool measures the thickness of fat at various points on your body. It is a cost-effective method but requires proper technique to ensure accuracy.
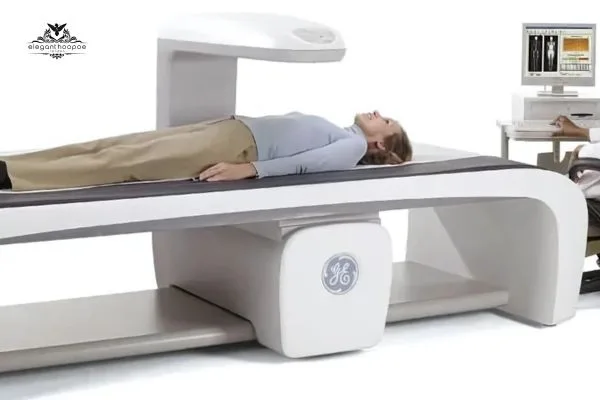
Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA)
A DEXA scan provides a detailed analysis of body composition, including fat, lean mass, and bone density. It’s considered one of the most accurate methods for determining fat to muscle ratio, but it tends to be more expensive and typically performed in clinical settings.
Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA)
BIA measures body composition by sending a small electrical current through the body. While easy and convenient, the accuracy of BIA can be affected by factors such as hydration levels.
Strategies for Achieving the Perfect Fat to Muscle Ratio
Once you understand your current fat to muscle ratio, the next step is to implement strategies to optimize it. Here are some effective approaches:
Strength Training for Muscle Building
Strength training is the most effective way to increase muscle mass and improve your fat to muscle ratio. Resistance exercises like weightlifting, bodyweight workouts, and resistance bands target muscles and stimulate growth. Incorporating compound movements such as squats, deadlifts, and bench presses will provide the greatest benefits in muscle development.
Key Focus: Aim for at least 2–3 strength training sessions per week, targeting different muscle groups for balanced muscle development.
Cardio to Burn Fat
While building muscle is essential, reducing excess fat through cardiovascular exercise is also crucial. Cardio exercises such as running, cycling, swimming, and HIIT (high-intensity interval training) can help burn fat while preserving lean muscle mass.
Key Focus: Include at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity cardio per week or 75 minutes of high-intensity cardio to promote fat loss.
Optimize Nutrition with Protein
Diet plays a crucial role in achieving the ideal fat to muscle ratio. Protein is the building block of muscle, and consuming adequate protein helps in muscle recovery and growth. Additionally, a diet that supports fat loss without sacrificing muscle mass is essential.
Key Focus: Aim for a protein intake of 0.8 to 1.2 grams per pound of body weight. Include lean protein sources such as chicken, turkey, fish, eggs, and plant-based options like tofu and lentils.
Caloric Deficit with Muscle Preservation
To lose fat, you must create a caloric deficit—consuming fewer calories than your body needs. However, drastic caloric cuts can lead to muscle loss. To preserve muscle while losing fat, focus on a moderate deficit and combine it with strength training and high-protein intake.
Key Focus: A caloric deficit of 10–20% below your maintenance level will help reduce fat without compromising muscle mass.
Prioritize Recovery and Sleep
Muscle growth happens during rest, not while working out. Proper recovery, including getting 7–9 hours of quality sleep each night, is essential for muscle repair and growth. Without sufficient recovery time, your progress in building muscle will be significantly hampered.
Key Focus: Incorporate rest days into your workout routine, and ensure you’re getting enough sleep for optimal muscle recovery.

Conclusion: All About Fat to Muscle Ratio
Achieving the perfect fat to muscle ratio is a journey that requires a combination of strength training, cardiovascular exercise, proper nutrition, and adequate rest. By understanding the science behind body composition balance and taking consistent action, you can achieve the body composition that supports both aesthetics and overall health.
Remember that the ideal fat to muscle ratio will vary from person to person, but the principles of muscle building, fat loss, and healthy living remain universal. Patience, consistency, and the right strategies will ultimately help you achieve the balance you’re striving for.
References
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI-Assessing Your Weight and Health Risk







