What Is a Normal BMI and How Can You Maintain It for Better Health?
A normal BMI falls between 18.5 and 24.9, indicating a healthy weight range. Use a BMI calculator to check yours, then follow these simple tips to maintain it:
🥗 Eat a balanced diet with whole foods
🏃♀️ Exercise regularly, including cardio & strength training
🛌 Get 7–9 hours of sleep nightly
🍽️ Watch portion sizes & practice mindful eating
🧘♂️ Manage stress to prevent weight gain
While BMI is useful, it doesn’t reflect muscle mass or fat distribution—so use it alongside other health indicators.
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a widely used measure to determine if an individual’s weight is within a healthy range relative to their height. Therefore, a normal BMI calculator serves as a useful screening tool for identifying potential health risks associated with being underweight, overweight, or obese, even though BMI is not a direct measure of body fat.
In this article, we’ll explore what constitutes a normal BMI, how it is calculated, its significance, limitations, and how you can easily check yours using an easy BMI calculator.
What is BMI?

BMI is a numerical value derived from a person’s height and weight. Consequently, it is used globally as an indicator to classify individuals into different categories:
- Underweight
- Normal weight
- Overweight
- Obese
BMI Calculation Formula
Body Mass Index is a measure of body fat based on weight and height. You can calculate it using either the metric system or the US customary system.
1. Metric System (kg & meters)
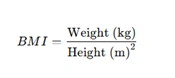
For example, a person weighing 70 kg and 1.75 m tall:
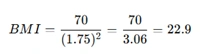
2. US Customary System (lbs & inches)
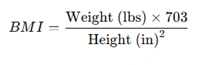
For example, a person weighing 154 lbs and 69 inches (5’9” tall):
A Body Mass Index between 18.5 and 24.9 is considered a healthy weight.
Understanding BMI Ranges
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO), Body Mass Index is classified into the following categories:
| BMI Range | Category |
| < 18.5 | Underweight |
| 18.5 – 24.9 | Normal Weight |
| 25 – 29.9 | Overweight |
| 30 – 34.9 | Obesity Class I |
| 35 – 39.9 | Obesity Class II |
| > 40 | Obesity Class III (Severe) |
Why You Should Use a Healthy BMI Calculator
Using a normal BMI calculator is essential because it helps assess health risks associated with weight. Specifically, a Body Mass Index outside the normal range can increase the likelihood of:
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Type 2 diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Stroke
- Osteoarthritis
- Sleep apnea
- Certain types of cancer
As a result, maintaining a healthy BMI reduces the risk of these conditions, promoting overall well-being.
How to Calculate Your Body Mass Index Using an Easy BMI Calculator
Using an easy BMI calculator is the simplest way to determine your Body Mass Index without manual calculations. To do so, just follow these steps:
- Enter your weight (in kg or lbs).
- Enter your height (in meters or inches).
- Click calculate, and the tool will instantly display your Body Mass Index and category.
Ultimately, a healthy BMI calculator helps assess your weight status, making it easier to track progress and maintain good health. You can easily use ours below to get more info about your health status right here, right now.
Weight
Height
Age

Limitations of BMI
Although widely used, Body Mass Index has several limitations:
1. Does Not Differentiate Between Fat and Muscle
Body Mass Index does not distinguish between muscle and fat. Thus, athletes or bodybuilders may have a high BMI but low body fat.
2. Does Not Consider Fat Distribution
Visceral fat (around organs) is more harmful than subcutaneous fat (under the skin), yet Body Mass Index does not account for fat location.

3. Varies Among Different Ethnicities
BMI’s health implications can differ among ethnic groups. For example:
- Asians may face higher risks of heart disease at lower Body Mass Index levels.
- African Americans may have more muscle mass, resulting in a higher Body Mass Index without excess fat.
4. Not Suitable for Certain Populations

Body Mass Index may not be accurate for:
- Children
- Elderly individuals
- Pregnant women
- Highly muscular individuals
Alternative Health Assessment Methods
Since Body Mass Index alone is not a perfect measure, consider additional health indicators:
1. Waist-to-Height Ratio
Studies suggest that waist circumference in proportion to height is a better health risk predictor than Body Mass Index.
2. Body Fat Percentage
Measuring body fat percentage generally provides a more accurate assessment of body composition.
3. Waist-to-Hip Ratio
A high waist-to-hip ratio indicates a higher risk of metabolic diseases.

How to Maintain a Healthy BMI Using a Normal BMI Calculator
If your BMI falls outside the normal range, follow these tips to achieve a healthy weight:
1. Eat a Balanced Diet
- First, focus on whole foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Then, limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and refined carbs.
2. Exercise Regularly
- Engage in 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise per week.
- Additionally, include strength training to build muscle and improve metabolism.
3. Monitor Portion Sizes
- Use smaller plates to prevent overeating.
- Practice mindful eating by chewing slowly and listening to hunger cues.

4. Get Enough Sleep
- Poor sleep is linked to weight gain and metabolic issues.
- Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
5. Manage Stress
- High stress increases cortisol levels, contributing to weight gain.
- Therefore, practice meditation, deep breathing, or yoga to stay balanced.

Conclusion: Normal BMI
A healthy BMI calculator is a helpful tool for evaluating weight status, but it should be used alongside other health assessments. While BMI provides a general guideline, factors like muscle mass, fat distribution, and lifestyle choices play a crucial role in overall health.
To summarize, to maintain a healthy weight, focus on balanced nutrition, regular exercise, quality sleep, and stress management. If you’re unsure about your Body Mass Index results, consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)-Adult BMI Categories
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)-Calculate Your Body Mass Index








