How Often Do Athletes Get IV Therapy, and Is It Worth It?
- Athletes use IV therapy for hydration, electrolyte replenishment, and nutrient restoration after intense training or competition.
- Frequency varies: once or twice a month for general athletes, more for high-endurance sports.
- Benefits include:
- Faster muscle recovery
- Boosted energy levels
- Improved immune function
- Should be done under medical supervision and in compliance with sports regulations.
Nowadays, IV therapy is frequently being used by athletes to improve their hydration, electrolytes restoration, and receive vital vitamins and minerals that may support optimal health, performance, and overall well-being. Saline solutions, electrolytes, amino acids, and antioxidants can all be used in the mixture as treatments to help muscle repair, fatigue reduction, and dehydration elimination that may result from intense training or competition. Although the outcome and effects on various individuals may differ, almost all athletes claim positive outcomes they have seen following each IV treatment session.
Read about Home IV therapy
Benefits of IV therapy for athletes
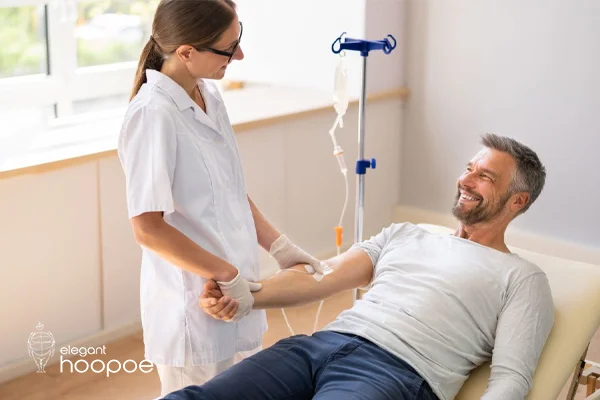
Generally, athletes can benefit from IV therapy in several ways, including, but not limited to, faster rehydration, better delivery of nutrition, and shorter time for recovery. It helps the athletes regain their optimum energy levels, lessen muscle pains, and restore vital vitamins and minerals lost during intense training or competition.
Additionally, IV therapy can help individuals flush out toxins, boost immunity, reduce the risk of sickness, and improve overall performance by supplying particular nutrition and hydration demands. Overall, IV therapy can be considered a valuable tool for athletes who are aiming to maximize their training and competition readiness.
Which group of athletes can take IV drips?
IV therapy is widely used by a different group of sports teams, including football, basketball, and soccer teams, bodybuilders, weightlifters, and generally all athletes who are engaging in high-intensity training, particularly those in high-endurance sports like marathon runners, triathletes, and cyclists.
It is frequently used to improve recovery from breathtaking training sessions or contests, which helps individuals to restore nutrients and rehydrate quickly. However, it’s crucial to remember that using IV therapy should first be discussed with a medical practitioner and then adhered to by sports rules, as some administrations may be limited or outright forbidden by organizations like as the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA).
Related article: IV Therapy Side Effects
Minerals and vitamins blended in IV therapy for athletes
A blend of vital vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C, magnesium, calcium, potassium, zinc, and vitamin B complex (containing B6 and B12), are normally administered by IV therapy to athletes. These nutrients are used to improve overall performance, assist muscle repair, decrease fatigue, and improve hydration. To help muscle recovery, certain formulations may also contain amino acids like glutamine or branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs)
Different types of IV Drips for athletes?

Athletes can get a variety of IV drips that are customized to fit their individual needs:
- Hydration Drips: These drips which usually include saline solutions help the athletes with rapid replenishment and fluid balancing against dehydration resulting from intense exercise.
- Vitamin and Mineral Infusions: High-dose vitamin drips, such as those that contain magnesium, vitamin C, and B vitamins, can improve the immune system, increase energy, and lessen cramping in the muscles.
- Electrolyte replenishment: IV drips containing electrolytes such as calcium, potassium, and salt that aim to restore the balance of vital minerals lost through high levels of sweating after extended periods of physical exertion.
- Amino Acid Infusions: To help in muscle fatigue recovery, lessen soreness, and encourage protein synthesis after exercise, these drips contain branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs).
- Antioxidant Treatments: Glutathione and other antioxidant-rich drips can help lessen the oxidative stress and inflammation resulting from intense exercise.
- Performance-Enhancing Formulas: To improve athletic performance, endurance, and general recovery, certain specialized drips may contain a mix of vitamins, minerals, and amino acids.
Depending on the sport, intensity level, and particular health goals of the athlete, each type of IV drip can be tailored to meet their specific requirements.
See also IV Hydration Therapy Benefits

IV Treatment affects the durability of athletes
Considering the kind of nutrients given, the specific athlete’s metabolism, and their level of physical activity, one can come up with a series of effects that might result from the use of IV therapy. Hydration and electrolyte recovery may usually occur within a few hours to a few days; whereas, vitamin and mineral retention might take longer, usually lasting several days to weeks, depending on the specific nutrient and the athlete’s nutritional state. On the other hand, regular attendance is usually advised for long-term advantages, especially during times of intense training or competition.
Things to do before and after IV session
Athletes should pay attention to this crucial advice and take the following precautions before and after IV therapy:
- Speak with a Healthcare Professional: To ensure the safety and suitability of the IV formulation, it is advised to consult with a healthcare professional about any allergies, medical problems, or prescriptions,
- Hydration: Properly hydrated bodies respond better to IV Therapy,
- Eat Lightly: To sustain energy levels and prevent any possible dizziness, it is better to eat a light breakfast or lunch before taking IV therapy session,
- Monitor Response: It is advised to keep an eye on how the body reacts to the therapy,
- Hydrate: Keep up your fluid consumption to stay hydrated, especially if you plan to exercise afterward.
- Rest and Recovery: After a workout, give your body time to assimilate the nutrients and recover as much as possible.
- Stay away from intense activities as soon as possible: After therapy, take a little break from intense exercise to give your body time to adjust.
Athletes can optimize the benefits of IV therapy by following these guidelines.
Food and nutrition that can be consumed after taking IV therapy

Athletes should focus on eating meals that promote healing, restore nutrients, and keep them hydrated after IV treatment. Optimal choices consist of:
- Hydrating Foods: Fruits and vegetables high in water content, such as watermelon, cucumbers, oranges, and strawberries,
- Complex Carbohydrates: Whole grain bread, sweet potatoes, brown rice, and quinoa,
- Lean Proteins: Fish, tofu, chicken, turkey, and beans,
- Healthy Fats: Avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil,
- Electrolyte-Rich Foods: Nuts, seeds, bananas, and spinach.
Generally, these elements in a well-balanced diet combined with sufficient water can maximize recovery and improve performance.
Intense training immediately after taking an IV therapy session
Immediately after an IV therapy session, athletes should refrain from intense training or competitive events. It is best to give the body time to adapt and efficiently absorb the nutrients. Engaging in intense activities right after may lead to fatigue, dehydration, or an adverse reaction due to the sudden intake of fluids and nutrients.
Rest time, which may be anything from a few hours to a day, helps athletes to have optimum recovery and reduce the possibility of negative side effects, which ultimately enables them to compete at their best without putting unnecessary pressure on their bodies.
Read more about How do you Feel After IV Therapy?
Conclusion, is IV treatment a good choice for athletes?
In summary, IV therapy is a good option for athletes seeking to accelerate their rehydration and effective nutrition delivery to enhance recovery, performance, and general well-being. Any group of athletes may feel the need to have at least one or two sessions of IV therapy within a month; however, athletes who train hard or compete might benefit more from its capacity to improve hydration and restore lost nutrients.