How Does Tongue Gesture Recognition Enable Hands-Free Device Control?
=Tongue gesture recognition is Microsoft’s innovative hands-free tech that lets users control digital devices using subtle tongue movements. It’s designed especially to assist people with disabilities and overcome the limits of voice, touch, or gaze-based inputs. Here’s how it works and why it matters:
Inertial sensors detect tongue movements and translate them into commands
Machine learning ensures accurate recognition of gestures like tapping teeth or cheek touches
Major benefits: Boosts independence, privacy, and accessibility
Key applications:
Assistive tech for motor impairments
Rehab and medical device control
Hands-free use in VR, AR, and personal computing
Secure input in sensitive environments
Tongue gesture recognition could revolutionize how we interact with technology—making it more inclusive, discreet, and intuitive.
Imagine a future where controlling your digital devices is as simple as moving your tongue. This vision is now closer to reality with a groundbreaking patent that harnesses tongue gestures for hands-free interaction that will make people with disabilities’s lives much easier. Thanks to our collaboration with David from @xleaks7, we spotted Microsoft’s new patent explaining the tongue gesture recognition technology.
The Problem the Patent Is Going to Solve:
Traditional input methods like touchscreens, keyboards, and even voice commands have their limitations, especially for users whose hands are occupied or those with motor impairments.
Existing technologies such as speech recognition and gaze tracking, while useful, also come with their set of challenges, including privacy concerns and environmental limitations.
The patent aims to address these gaps by introducing a novel method – tongue gesture recognition – as a means of seamless interaction with computing devices.
How the Tongue Gesture Recognition Works:
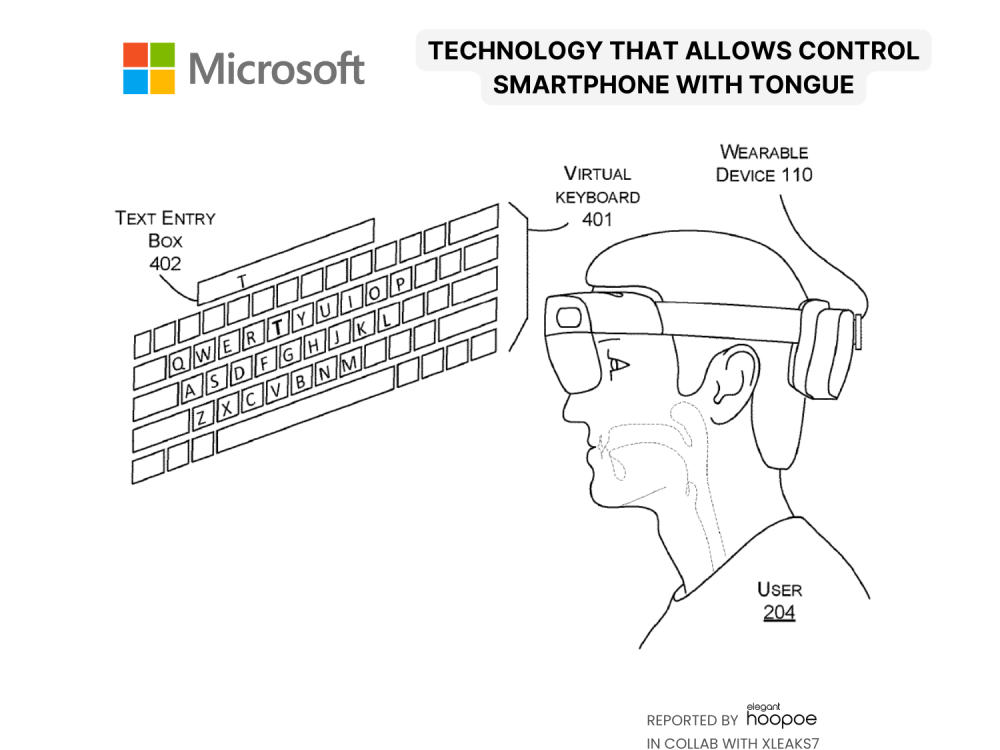
At its core, the technology utilizes inertial sensors, specifically inertial measurement units (IMUs), to capture subtle motion signals generated by tongue movements.
These sensors, integrated into devices like head-worn displays, earbuds, or even cochlear implants, detect and translate tongue gestures into commands that control various applications and functionalities.
Machine learning plays a pivotal role here, where algorithms are trained to accurately recognize specific tongue gestures based on the patterns observed in the motion signals.
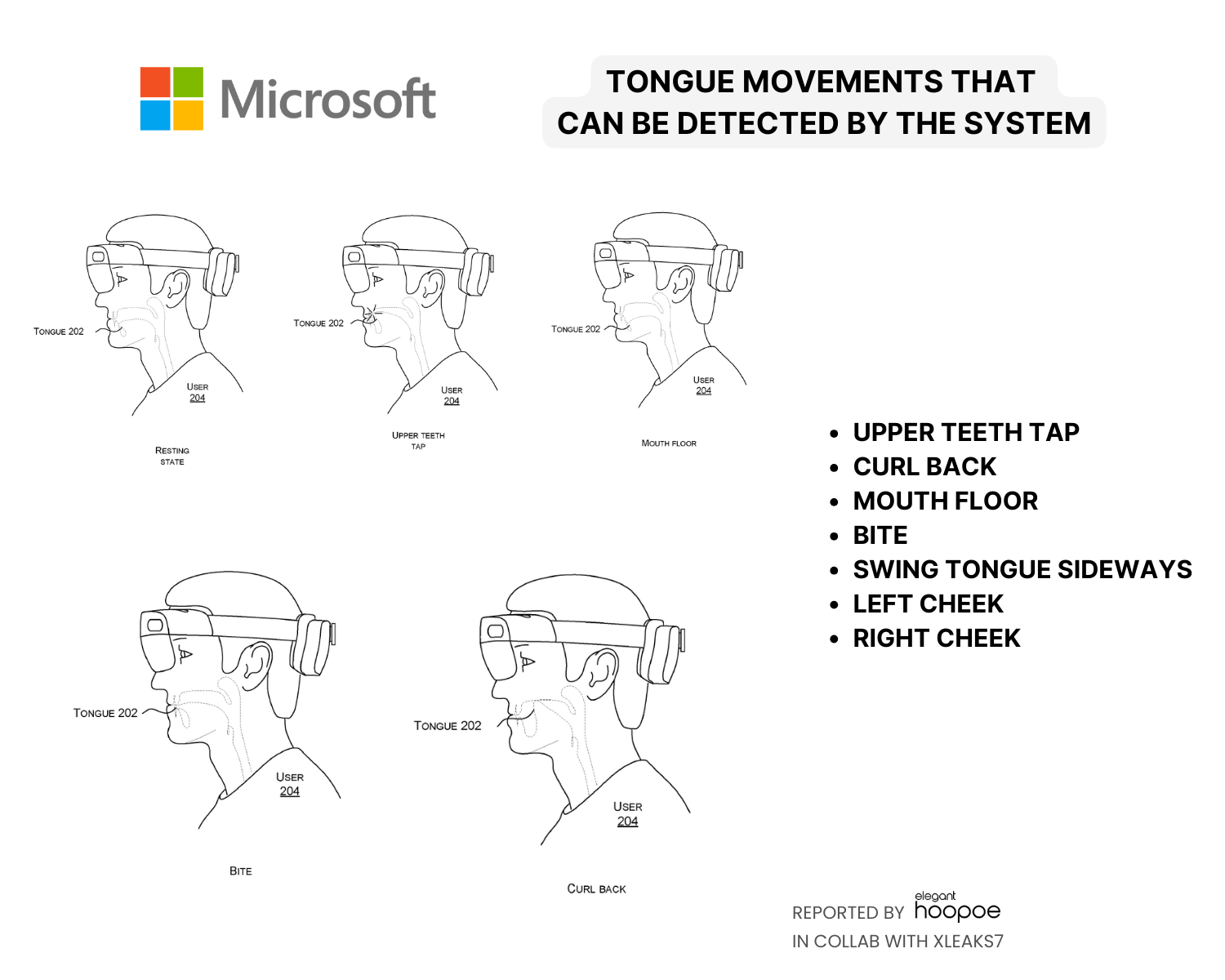
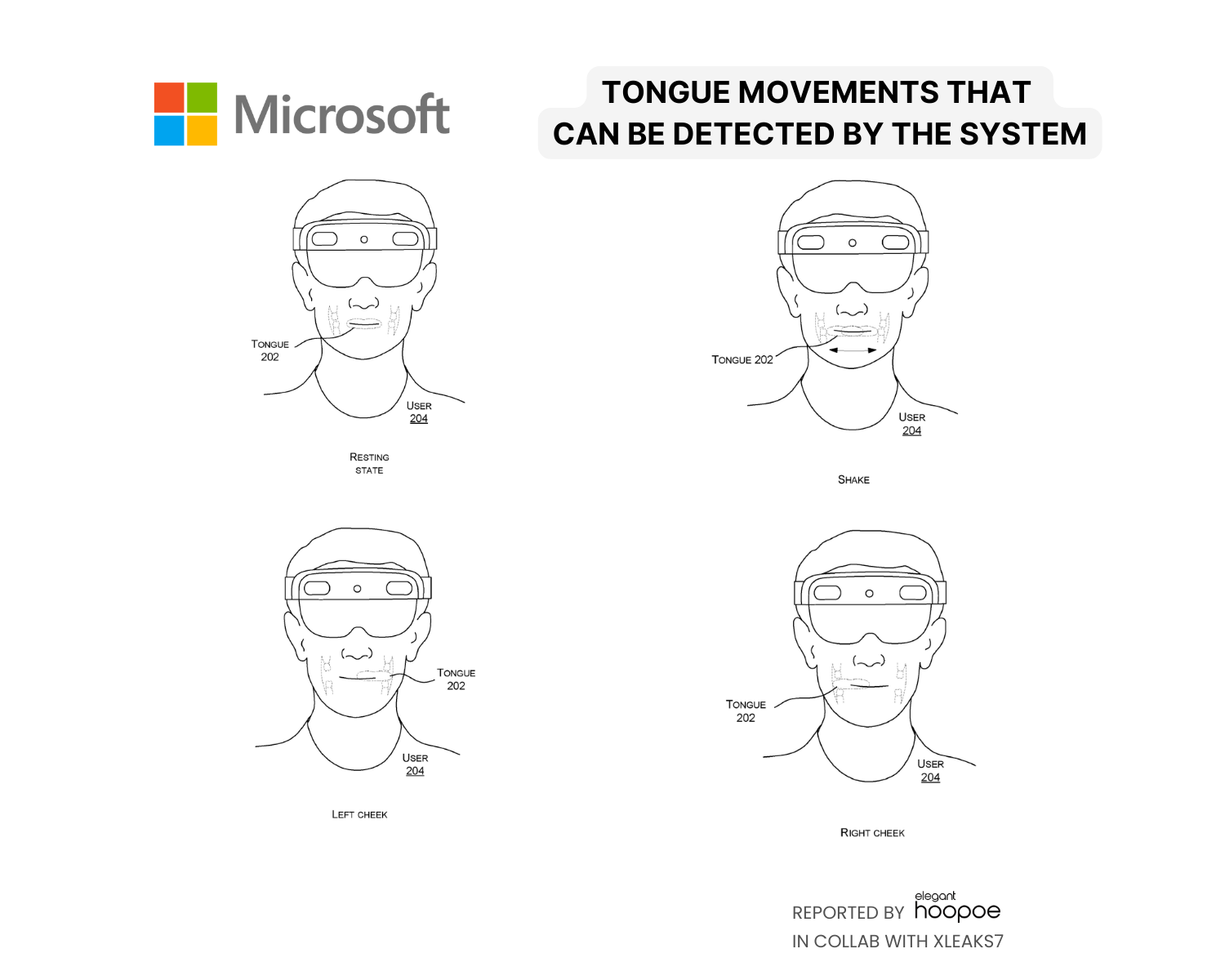
Tongue Gestures that can be identified by the System
- Upper teeth tap
- Curl back
- Mouth floor
- Bite
- Swing tongue sideways
- Left cheek
- Right cheek
Tongue Gesture Recognition Benefits for Users with Disabilities
This innovation offers transformative benefits for users with disabilities:
- Independence: Enables individuals with physical disabilities to operate devices independently, bypassing the need for traditional input methods
- Privacy: Facilitates interaction in quiet settings without the need for audible commands, respecting personal space and privacy
- Accessibility: Provides a universal interface that is accessible to a wide range of disabilities, including conditions that affect motor skills or vocal abilities
- Integration: Integrates seamlessly with existing wearable technology, leveraging familiar devices to enhance functionality
Possible Applications of Tongue Gesture Recognition
The patent for detecting tongue gestures presents numerous potential applications across diverse fields, particularly benefiting individuals with disabilities. Here are some key areas where this technology could make a significant impact:
Accessibility Technology:
- Motor Impairments: People with motor impairments, who may struggle with traditional input methods like keyboards or touchscreens, can benefit from hands-free interaction using tongue gestures
- Spinal Cord Injuries: Users with limited hand and arm mobility due to spinal cord injuries can control devices effortlessly through tongue gestures
- Prosthetic Limbs: Tongue gestures offer a precise and intuitive control option for prosthetic limbs, enhancing functionality and usability
Healthcare Applications of Tongue Gesture Recognition:
- Assistive Technology: Tongue gesture recognition can assist individuals with disabilities in managing medical devices, environmental controls (such as lights and temperature), and communication aids
- Rehabilitation: In rehabilitation settings, integrating tongue gestures into therapy devices or exercises can aid patients recovering from stroke or neurological conditions
Virtual and Augmented Reality:
- Gaming and Entertainment: Tongue gestures enhance gaming experiences in virtual reality (VR), allowing users to interact seamlessly within virtual environments
- Training Simulations: In augmented reality (AR), tongue gestures facilitate hands-free interaction with virtual objects during training simulations, applicable in fields like surgery, maintenance, and military training
Tongue Gesture Recognition for Personal Computing:
- Productivity Tools: Tongue gestures integrated into productivity applications such as word processors and spreadsheets enable users to navigate and manipulate content without physical touch
- Multitasking: Users engaged in hands-on activities like cooking or workshop tasks can control devices via tongue gestures, maintaining workflow efficiency
Privacy and Security:
- Tongue gesture recognition offers a secure input method, reducing the risk of unintended commands or privacy breaches compared to voice recognition, particularly in sensitive environments
NOTE TO EDITORS: The text and visuals of this article are the intellectual property of Elegant Hoopoe. If you want to share the content, please give a proper clickable credit. Thanks for understanding.