Weight
Height
Age

Body Mass Index (BMI) is a numerical value derived from an individual’s height and weight, serving as a general measure of body composition. A BMI calculator is commonly used for men and women to show the healthy weight for your height by assessing whether a person’s weight is appropriate for their height and age.
The BMI score categorizes individuals into different weight classifications, including underweight, normal weight, overweight, and obese, based on established thresholds. These classifications may vary depending on factors such as age and geographic region and can also be broken down into more specific subgroups, such as severely underweight or extremely obese.
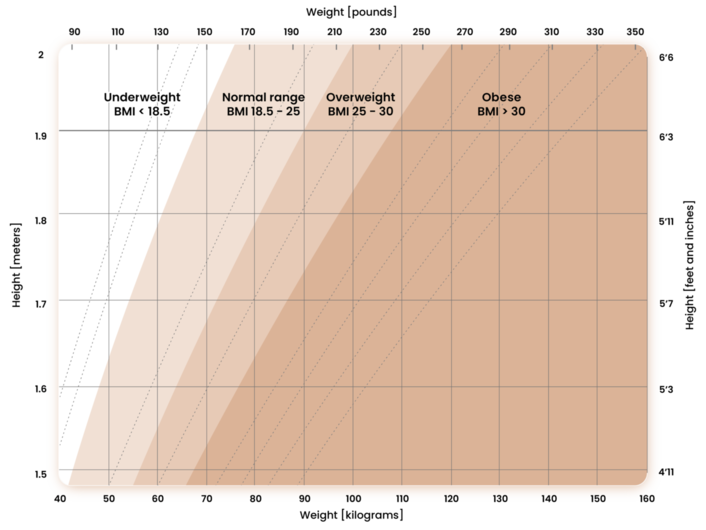
While BMI does not provide a perfect assessment of health, as it does not distinguish between muscle and fat mass, it remains a practical tool for identifying potential weight-related health risks and determining if further evaluation is necessary. Below, you can find the BMI scales used for classification, encouraging you to use a BMI calculator to track your weight loss plans.
The World Health Organization (WHO) provides recommended body weight guidelines for adults based on BMI scores. These guidelines apply to individuals age 20 or older, regardless of gender.
| Categories | BMI range – kg/m2 |
| Severely Thin | < 16 |
| Moderately Thin | 16 – 17 |
| Mildly Thin | 17 – 18.5 |
| Normal | 18.5 – 25 |
| Overweight | 25 – 30 |
| Class I Obesity | 30 – 35 |
| Class II Obesity | 35 – 40 |
| Class III Obesity | > 40 |
This graph shows BMI categories based on WHO data. The dashed lines indicate subdivisions within each category.
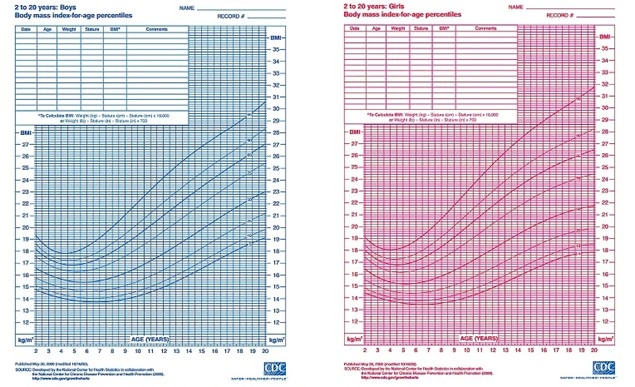
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) advises the use of BMI categorization for children and adolescents aged 2 to 20 years.
| Category | Percentile Range |
| Underweight | <5% |
| Healthy weight | 5% – 85% |
| At risk of overweight | 85% – 95% |
| Overweight | >95% |
You can determine your child’s health status using a pediatric BMI calculator. The BMI-for-age percentiles growth charts provided by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) are as follows:
Overweight individuals face higher risks of serious diseases and health conditions, making it more important to check your status frequently with a BMI calculator. According to the CDC, here are some of those risks:

As illustrated by the aforementioned list, there are numerous adverse, and in some instances fatal, consequences associated with being overweight. It is generally advisable for individuals to maintain a BMI score below 25 kg/m². If the BMI calculator shows you’re not categorized in the healthy BMI range, it is preferable to consult a healthcare professional to determine if any lifestyle modifications are necessary to improve your overall health.
Avoiding obesity is not the only reason to use a BMI checker. There are specific health risks associated with being underweight, which are listed below:
In certain situations, being underweight may indicate an underlying condition or disease, such as anorexia nervosa, which carries its own risks. It is advisable to consult a doctor if the BMI calculator for women or men shows they are underweight, especially if the cause is not clear.
BMI is a commonly used indicator of healthy body weight for males and females but has some limitations. It provides an estimate without accounting for body composition. Since there is a wide variety of body types and distributions of muscle, bone mass, and fat, the BMI score should be considered alongside other measurements rather than as the only method for determining a person’s body weight.
BMI may not provide a fully accurate assessment as it measures excess body weight rather than excess body fat. Various factors, including age, sex, ethnicity, muscle mass, body fat, and activity level, influence BMI. For instance, an older individual who maintains a healthy weight but leads a sedentary lifestyle may possess significant amounts of excess body fat, which is unhealthy despite their weight. Conversely, a younger individual with the same BMI but with higher muscle composition would be considered healthy. This discrepancy is also evident in athletes, particularly bodybuilders, who might be classified as overweight due to their muscle mass, which is heavier than fat. In such cases, they could actually be at a healthy weight relative to their body composition. According to the CDC:
The limitations of BMI in assessing body fat are relevant to both adults and children. Furthermore, factors such as height and sexual maturation can influence BMI and body fat in children. BMI is a more accurate indicator of excess body fat in obese children than in overweight children, whose elevated BMI score may result from increased levels of either fat or fat-free mass (comprising water, organs, muscle, etc.). In lean children, variations in BMI can also be attributed to differences in fat-free mass.
Nevertheless, BMI remains a fairly reliable indicator of body fat for 90-95% of the population and can be effectively utilized in conjunction with other measures to determine an individual’s healthy body weight.
Below are the equations used for calculating BMI in the International System of Units (SI) and the US Customary system (USC) using a 5’10”, 160-pound individual as an example:

There’s no reason for you to understand the math, though. Simply calculate your BMI using our online Body Mass Index calculator at elegant hoopoe in just a few clicks. If you need help reaching your ideal BMI, feel free to book an appointment with our experts at our weight loss clinic in Dubai and transform your life.